Boosting testosterone naturally with TestoXLR8Pro™
January 8th, 2021By Leslie J. Farer
Maximizing testosterone levels is a prime objective of bodybuilders intent on increasing muscle mass and strength as well as other athletes seeking to gain a competitive edge and rise to the top of their game. And for good reason. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, has been shown to produce powerful anabolic (muscle building) and performance-enhancing effects. But it’s not just athletes who can benefit from optimizing their hormone levels; so can antiaging enthusiasts − both men and women over 40 − who wish to prevent physical decline, improve muscle mass and bone density, avoid age-related diseases, and enhance libido and general well-being. Although hormone replacement therapy is frequently the go-to approach for restoring hormones depleted by aging, like testosterone, research shows that it is possible to boost your body’s own testosterone production using specific nutrients. TestoXLR8Pro™ is a combination product containing multiple targeted and clinically tested ingredients that raise testosterone levels and optimize its metabolism in the body through a variety of diverse but complementary mechanisms for an overall additive and powerful effect.
Intro to Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary androgen (male sex hormone) in men, though it is present in women at lower levels. Testosterone is produced in mainly in the testes in men, and to a lesser extent in the ovaries in women and the adrenal glands in both genders. Besides its role in the development of secondary sex characteristics and sperm production in men, testosterone is important for both men and women for a variety of essential metabolic functions, including maintaining healthy bone and muscle mass, limiting fat accumulation, and enhancing libido, mood, and vitality.
Testosterone Levels Fall with Age, Raising Disease Risk Factors and Lowering Physical Function
Aging leads to significant declines in sex hormone production, including testosterone, (see figure 1). This has been linked toseveral negative consequences. A study on over 500 healthy men between 20 and 80 years old found that various forms of testosterone in the bloodstream (total testosterone, free testosterone, and bioavailable testosterone) decline continuously with age, starting in young adulthood, resulting in markedly lower levels in older men compared to young men. (1)
[Note: Most testosterone in the bloodstream is bound to one of two proteins, sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) or albumin. (We’ll see more on SHBG later.) A small percentage, known as ‘free’ testosterone, remains unbound in the bloodstream. Albumin-bound testosterone and free testosterone are the bioavailable forms (with the ability to act on target tissues); testosterone bound to SHBG is inactive. Total testosterone refers to the sum of free and bound testosterone.
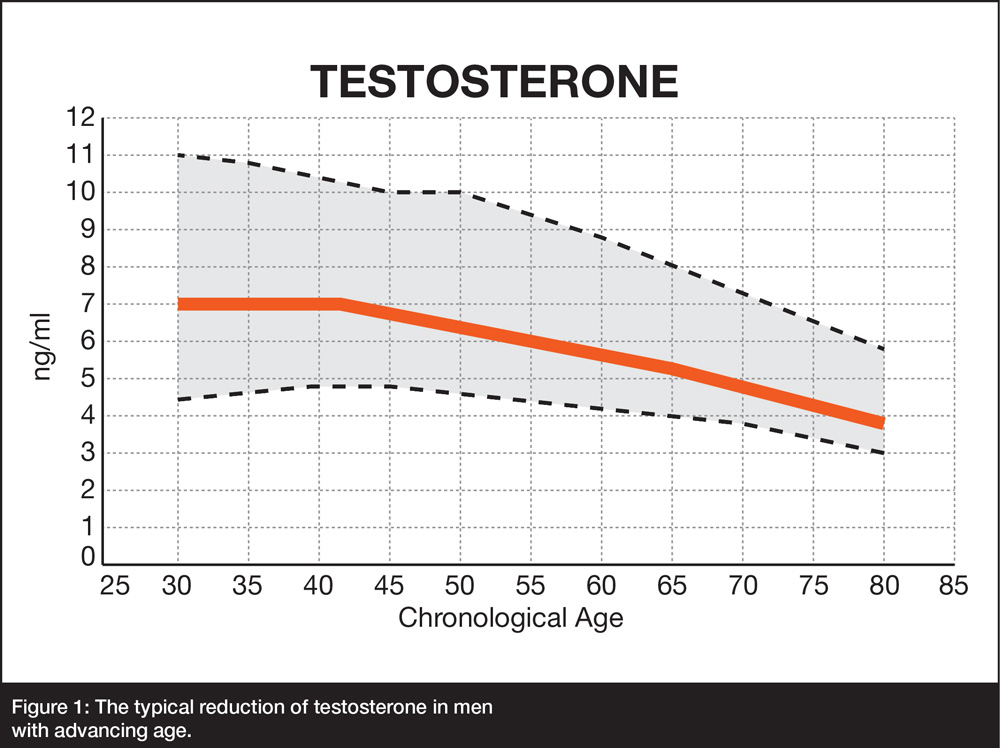
Figure 1: The typical reduction of testosterone in men with advancing age.
Steadily declining testosterone levels in men raisesmany risk factors includingatherosclerosis, (2-3) cardiovascular disease, (4-5) prostate cancer, (6-7) diabetes and insulin resistance, (8-9) depression, (10) cognitive deficits, (11-12) and decreased sex drive. (11) Levels of testosterone in women also fall with age (along with the significant decline of estrogen that occurs with menopause), which predisposeswomen to some of the same health risks. In addition, low testosterone negatively impacts body composition and can lead to decreased muscle mass and sarcopenia (the more marked loss of muscle mass and strength associated with aging), (11,13-15) reduced bone mineral density and osteoporosis, (11,16) increased abdominal fat, (11,8-9) and reduced physical function (17) in both men and women.
The good news is, restoring testosterone to more youthful levels ameliorates these negative effects, as we will see below. Since this issue of Aging Matters™ is devoted to sports and athletics, let us take a closer look at the beneficial effects of testosterone enhancement on body composition (especially muscle mass) and physical performance.
Testosterone Replacement Results in Muscle Mass Gains and Improved Performance
Several studies on adults over 60 years old show that testosterone replacement results in increased muscle mass and strength, reduced body fat, and enhanced exercise capacity. (13, 18-19) For example, in one of these studies, older men who used 1% testosterone gel for three years exhibited better stair-climbing power, improved chest and leg press performance, and greater lean body mass gains than men administered placebo. (18) These studies employed hormone replacement therapy using prescription testosterone gel, oral tablets, or capsules in order to raise testosterone levels. However, for those who choose not to use prescription hormone replacement, you can stimulate yourendogenous testosterone production safely and effectively and obtain the same positive improvements in muscle mass, strength, and fitness with the powerful synergy of nutrients in TestoXLR8Pro™. What sets this product apart from a slew of other testosterone-enhancers on the market is the science that backs up each nutrient, and the fact that most are present in clinically effective doses (i.e., doses used in clinical trials). Now let’s examine the studies that support each individual ingredient.
Shilajit, Fenugreek, and Stinging Nettle
Shilajit is a substance, found primarily in the Himalayas, formed over hundreds of years from the gradual decomposition of plants. Used primarily in Ayurveda, the traditional Indian system of medicine, shilajit can treat many conditions, including male infertility, and studies over the past decade show that it boosts testosterone levels. In a clinical trial on men between 45 and 55 years old, 250 mg shilajit taken twice a day (500 mg daily, the equivalent daily dose in TestoXLR8Pro™) for 90 days increased total and free testosterone as well as DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone), (20) a steroid hormone precursor that is a core component in most anti-aging regimens. In another study on infertile men, 100 mg shilajit administered twice daily for 90 days not only raised blood testosterone levels, but significantly improved sperm count. (21)
Another Ayurvedic ingredient, fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum), also known as Methi in India, is an annual herb in the pea family with a diverse array of active components and a long history of use in treating a broad spectrum of conditions. Fenugreek is thought inhibit two enzymes, aromatase and 5-alpha-reductase, (22) that lower testosterone by metabolizing it to estrogen (estradiol) and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), respectively. Elevated estrogen, like low testosterone, can lead to the development of breast tissue and increase the risk of heart attack, prostate cancer, and other conditions. DHT is highly potent, and increased levels are associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate cancer, and hair loss (since 5-alpha-reductase is also found in the scalp). By interfering with age-related increases in activity of aromatase and 5-alpha-reductase, fenugreek prevents conversion of testosterone to these undesirable metabolites. This action is important to older men in whom the activity of these enzymes tends to increase. A meta-analysis (a statistical analysis of several similar studies) on four clinical trials found that fenugreek extract has a significant effect on testosterone levels. (23)
In one trial on men 43 to 70 years old, 600 mg per day of fenugreek seed extract (slightly more than the 500 mg dose contained in TestoXLR8Pro™) for 12 weeks improved total and free testosterone levels as well as sexual function. (24) A similar study on women (20 to 49 years old) over eight weeks found similar results: 600 mg fenugreek seed extract per day also raised their free testosterone levels while improving libido and sexual function, (25) a positive ‘side effect’ for some people. And in a trial on men receiving 600 mg fenugreek seed extract per day during eight weeks of resistance training, the supplement was well tolerated and resulted in “significant anabolic [muscle synthesizing] and androgenic [male hormone-producing] activity as compared with the placebo.” It also led to a marked improvement in body fat percent. (26)
Stinging nettle (Urtica dioica) root is a well-researched phytotherapy, often used to treat BPH, which acts by multiple pathways, including inhibition of aromatasein prostate tissue. (27-28) The herb has been shown to increase testosterone levels (as well as sperm count and motility) in animals. (29)
Vitamin D
Research over the past several years has revealed the multiple and extensive health benefits of vitamin D, from promoting bone mineralization to supporting immune, cardiovascular, and cognitive health, to modulating sex hormone production and fertility. But the term “vitamin” D is somewhat of a misnomer, since technically, it is not a vitamin, but a prohormone (hormone precursor). Interestingly, vitamin D has been shown to influence testosterone levels in men. (30-32) A study on over 4,000 men to examine various metabolic disease risk factors found that lower 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels were associated withlower total testosterone levels. (31) [Note: 25-hydroxyvitamin D is the most abundant vitamin D metabolite in the blood and used in blood testing as an indicator of vitamin D status in the body.] Other studies show that vitamin D deficiency can lead to declines in muscle strength and function, and reduced physical performance, (33-34) probably at least in part due to vitamin D ‘s influence on testosterone levels.

Conversely, supplementing with Vitamin D can raise testosterone levels and improve performance. In a noteworthy trial on healthy overweight men who were initially vitamin D deficient and low in testosterone, supplementation with 83 ug (3332 IU) vitamin D daily for one year significantly raised their 25-hydroxyvitamin D as well as total and free testosterone levels. (30) Vitamin D supplementation may also reverse the negative effects of vitamin D deficiency on muscle strength and boost exercise capacity, as it did in older women with initial low baseline values. (19) In fact, one group of researchers proposes that maintaining 25-hydroxyvitamin D blood levels above the normal reference range could have a dramatic effect in raising testosterone levels, increasing muscle function and strength, and decreasing recovery time from training. (34)
[Note: TestoXLR8Pro™ contains the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for vitamin D for adults up to age 70, 600 IU. Your total vitamin D intake depends on the amounts contained in any other supplements you consume, such as a multi-vitamin, a vitamin D supplement, etc., the foods you eat, and the amount of sunlight you are exposed to (vitamin D is also synthesized in the skin in response to sunlight). The reference range for 25-hydroxyvitamin D is 20-100 ng/ml, with optimal blood levels in the approximate range of 50-80 ng/ml, which can only be determined by blood testing; it usually requires between 2000 and 5000 IU of ingested vitamin D to reach optimal levels. Do not consume high amounts of vitamin D (i.e., vitamin D intake that would result in 25-hydroxyvitamin D blood levels approaching or above 100 ng/ml, as suggested in this last study) without first consulting your health care professional, as high levels may be potentially toxic.]
Zinc and Boron
Zinc is an essential mineral crucial to multiple aspects of cellular metabolism and physiology, including the activity of over 100 enzymes, as well as immune function, protein synthesis, wound healing, growth and development, sexual function, and hormone modulation. Zinc is not stored in the body, so regular dietary intake is required. Studies have shown that low zinc levels are linked with low testosterone, sexual dysfunction, and infertility in men, (35-38) and that oral zinc supplementation raises testosterone levels. (35,38) In a study on men 55 to 73years oldwho were marginally zinc deficient, 30 mg zinc taken as an oral supplement for six months resulted in a doubling of their blood testosterone levels. (38)
[Note: TestoXLR8Pro™ contains 15 mg zinc (the RDA is 8 mg for women and 11 mg for men). Multivitamins typically contain 10 to 15 mg zinc, so if you take a multivitamin in addition to TestoXLR8Pro™, that will add up to approximately 25 to 30 mg zinc daily which is in the dose range of this last study. Check your multivitamin and other supplement labels carefully since the upper recommended limit for zinc is 40 mg per day.]
Boron is a trace mineral important to many aspects of health, including bone mineralization, inflammation reduction, antioxidant status, and sex hormone production. Although studies have shown conflicting results, a few do indicate that boron supplementation influences sex hormone levels in both men and women. A study on healthy male volunteers taking 10 mg boron daily for one week found significant increases in the men’s free testosterone levels accompanied by decreases in estradiol. (39) Researchers believe that boron may interfere with the chemical interactions between testosterone and SHBG (a protein that binds testosterone), essentially causing an “uncoupling” of the two, (40) which would explain the rise in free testosterone in the male volunteers. This unbinding action mediated by boron, which frees up biologically active testosterone, may be beneficial to aging men with elevated levels of SHBG and low free and total testosterone. In postmenopausal women, 3 mg boron per day markedly raised levels of both estradiol and testosterone. (41) Additionally, boron supplementation has been shown to increase blood levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in animals and humans, (42) which may be another mechanism by which boron raises testosterone. TestoXLR8PRO™ contains a source of soluble boron known as calcium fructoborate, a natural fructose-boron complex found in fruits and vegetables; a daily serving of TestoXLR8PRO™ provides 5 mg of elemental boron, which is in the range used in these studies.
TetraSOD®
Finally, the last ingredient we will discuss is superoxide dismutase (SOD), an antioxidant enzyme present in relatively high concentrations in the testes, where most testosterone is produced in men. Oxidative damage to tissues that manufacture testosterone may cause the hormone’s levels to decline with age; antioxidants such as SOD may help prevent this damage. SOD can also counter the increased oxidative stress associated with exercise. TestoXLR8Pro™ contains a concentrated source of SOD known as TetraSOD®, derived from a marine phytoplankton strain grown under patent-pending technology. A study on exercise capacity in young football players demonstrated that 25 mg TetraSOD® (the equivalent dose in TestoXLR8Pro™) taken daily for one month improved several blood markers of oxidative stress and enhanced athletic performance. (43)
Putting it All Together
We have covered a lot of territory. First, we examined the negative impact of aging on sex hormone production (lowered testosterone, in particular) which results in the development of a variety of age-related diseases as well as physical declines such as bone and muscle loss and reduced function in both men and women. Next, we learned that, thankfully, there is something we can do about it. Research has demonstrated that restoring testosterone to more youthful levels can ameliorate and even reverse these negative consequences of aging, leading to gains in muscle mass and strength and improved physical performance in both sexes.
Hormone replacement therapy is often the first-line approach to restore deficient hormones, but there’s a safe, effective, and prescription-free alternative − the combination of targeted and clinically tested nutrients in TestoXLR8Pro™. Most ingredients in the formulation are in the dose ranges used in clinical studies and, as we just reviewed, each one individually has been shown to influence endogenous testosterone levels; combined they exert an overall potent and synergistic effect. Some nutrients directly stimulate testosterone manufacture, while others block age-related processes that can deplete the hormone, such as binding to SHBG or conversion by enzymes to estrogen and DHT. Together, these various mechanisms improve and “revitalize” your biochemistry, promoting higher levels of free and total testosterone in your bloodstream for noticeable gains in mass, strength, and performance, with additional benefits to overall health.
TestoXLR8Pro™ should be taken at a dose of one capsule three times daily. For best results, use as part of a comprehensive program which includes a healthy diet with ample servings of protein coupled with an exercise program with strength/weight training at least three times a week.
There are dozens of testosterone-enhancers to choose from, but TestoXLR8Pro™, with its unique combination of clinically proven and multi-acting ingredients, is a cutting-edge product that will support your performance goals and general health.
References
1. Leifke E, Gorenoi V, Wichers C, Von Zur Mühlen A, Von Büren E, Brabant G. Age-related changes of serum sex hormones, insulin-like growth factor-1 and sex-hormone binding globulin levels in men: cross-sectional data from a healthy male cohort. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2000 Dec;53(6):689-95.
2. Hak AE, Witteman JC, de Jong FH, et al. Low levels of endogenous androgens increase the risk of atherosclerosis in elderly men: the Rotterdam study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Aug;87(8):3632-9.
3. Jones RD, Nettleship JE, Kapoor D, Jones HT, Channer KS. Testosterone and atherosclerosis in aging men: purported association and clinical implications. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005 5(3):141-54.
4. Malkin CJ, Pugh PJ, Morris PD, Asif S, Jones TH, Channer KS. Low serum testosterone and increased mortality in men with coronary heart disease. Heart. 2010 Nov;96(22):1821-5.
5. Ohlsson C, Barrett-Connor E, Bhasin S, et al. High serum testosterone is associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular events in elderly men. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Oct 11;58(16):1674-81.
6. Morgentaler A, Rhoden EL. Prevalence of prostate cancer among hypogonadal men with prostate-specific antigen levels of 4.0 ng/mL or less. Urology. 2006 Dec;68(6):1263-7.
7. Hoffman MA, DeWolf WC, Morgentaler A. Is low serum free testosterone a marker for high grade prostate cancer? J Urol. 2000 Mar;163(3):824-7.
8. Chen RY, Wittert GA, Andrews GR. Relative androgen deficiency in relation to obesity and metabolic status in older men. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006 Jul;8(4):429-35.
9. Abate N, Haffner SM, Garg A, Peshock RM, Grundy SM. Sex steroid hormones, upper body obesity, and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Oct;87(10):4522-7.
10. Almeida OP, Yeap BB, Hankey GJ, Jamrozik K, Flicker L. Low free testosterone concentration as a potentially treatable cause of depressive symptoms in older men. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008 Mar;65(3):283-9.
11. Leder BZ,Rohrer JL, Rubin SD, Gallo J, Longcope C. Effects of aromatase inhibition in elderly men with low or borderline-low serum testosterone levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2004 Mar;89(3):1174-80.
12. Hogervorst E, Bandelow S, Combrinck M, Smith AD. Low free testosterone is an independent risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Gerontol. 2004 Nov-Dec;39(11-12):1633-9.
13. Wittert GA, Chapman IM, Haren MT, Mackintosh S, Coates P, Morley JE. Oral testosterone supplementation increases muscle and decreases fat mass in healthy elderly males with low-normal gonadal status. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003 Jul;58(7):618-25.
14. Yuki A, Otsuka R, Kozakai R, et al. Relationship between Low Free Testosterone Levels and Loss of Muscle Mass. Sci Rep. 2013 May 10;3:1818.
15. Yuki A, Ando F, Otsuka R, Shimokata H. Low free testosterone is associated with loss of appendicular muscle mass in Japanese community-dwelling women. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2015 Mar;15(3):326-33.
16. Burnett-Bowie SA, McKay EA, Lee H, Leder BZ. Effects of aromatase inhibition on bone mineral density and bone turnover in older men with low testosterone levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Dec;94(12):4785-92.
17. Chiang JM, Kaysen GA, Segal M, Chertow GM, Delgado C, Johansen KL. Low testosterone is associated with frailty, muscle wasting and physical dysfunction among men receiving hemodialysis: a longitudinal analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019 May 1;34(5):802-810.
18. Storer TW, Basaria S, Traustadottir T, et al. Effects of Testosterone Supplementation for 3 Years on Muscle Performance and Physical Function in Older Men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Feb 1;102(2):583-593.
19. De Spiegeleer A, Beckwée D, Bautmans I, Petrovic M; Sarcopenia Guidelines Development group of the Belgian Society of Gerontology and Geriatrics (BSGG). Pharmacological Interventions to Improve Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Older People: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses. Drugs Aging. 2018 Aug;35(8):719-734.
20. Pandit S, Biswas S, Jana U, De RK, Mukhopadhyay SC, Biswas TK. Clinical evaluation of purified Shilajit on testosterone levels in healthy volunteers. Andrologia. 2016 Jun;48(5):570-5.
21. Biswas TK, Pandit S, Mondal S, et al. Clinical evaluation of spermatogenic activity of processed Shilajit in oligospermia. Andrologia. 2010 Feb;42(1):48-56.
22. Nguyen SM, Ko Ko N, Sattar AS, Gucuk Ipek E, Ali S. Pulmonary Embolism Secondary to Testosterone-Enhancing Herbal Supplement Use. Cureus. 2017 Aug 6;9(8):e1545.
23. Mansoori A, Hosseini S, Zilaee M, Hormoznejad R, Fathi M. Effect of fenugreek extract supplement on testosterone levels in male: A meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytother Res. 2020 Feb 11.
24. Rao A, Steels E, Inder WJ, Abraham S, Vitetta L. Testofen, a specialised Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract reduces age-related symptoms of androgen decrease, increases testosterone levels and improves sexual function in healthy aging males in a double-blind randomised clinical study. Aging Male. 2016 Jun;19(2):134-42.
25. Rao A, Steels E, Beccaria G, Inder WJ, Vitetta L. Influence of a Specialized Trigonella foenum-graecum Seed Extract (Libifem), on Testosterone, Estradiol and Sexual Function in Healthy Menstruating Women, a Randomized Placebo Controlled Study.Phytother Res. 2015 Aug;29(8):1123-30.
26. Wankhede S, Mohan V, Thakurdesai P. Beneficial effects of fenugreek glycoside supplementation in male subjects during resistance training: A randomized controlled pilot study. J Sport Health Sci. 2016 Jun;5(2):176-182.
27. [No authors listed] Urtica dioica; Urtica urens (nettle). Monograph. Altern Med Rev. 2007 Sep;12(3):280-4.
28. Moradi HR, Erfani Majd N, Esmaeilzadeh S, Fatemi Tabatabaei SR. The histological and histometrical effects of Urtica dioica extract on rat’s prostate hyperplasia. Vet Res Forum. 2015 Winter;6(1):23-9.
29. Jalili C, Salahshoor MR, Naseri A. Protective effect of Urtica dioica L against nicotine-induced damage on sperm parameters, testosterone and testis tissue in mice. Iran J Reprod Med. 2014 Jun;12(6):401-8.
30. Pilz S, Frisch S, Koertke H, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on testosterone levels in men. Horm Metab Res. 2011 Mar;43(3):223-5.
31. Chen C, Zhai H, Cheng J, et al. Causal Link Between Vitamin D and Total Testosterone in Men: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Aug 1;104(8):3148-3156.
32. Lerchbaum E(1), Obermayer-Pietsch B. Vitamin D and fertility: a systematic review. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012 May;166(5):765-78.
33. Książek A, Zagrodna A, Słowińska-Lisowska M. Vitamin D, Skeletal Muscle Function and Athletic Performance in Athletes-A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2019 Aug 4;11(8):1800.
34. Dahlquist DT, Dieter BP, Koehle MS. Plausible ergogenic effects of vitamin D on athletic performance and recovery. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Aug 19;12:33.
35. Vecchio M, Navaneethan SD, Johnson DW, et al. Interventions for treating sexual dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Dec 8;(12):CD007747.
36. Fallah A, Mohammad-Hasani A, Colagar AH. Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men’s Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization. J Reprod Infertil. 2018 Apr-Jun;19(2):69-81.
37. Khedun SM, Naicker T, Maharaj B. Zinc, hydrochlorothiazide and sexual dysfunction. Cent Afr J Med. 1995 Oct;41(10):312-5.
38. Prasad AS, Mantzoros CS, Beck FW, Hess JW, Brewer GJ. Zinc status and serum testosterone levels of healthy adults. Nutrition. 1996 May;12(5):344-8.
39. Naghii MR, Mofid M, Asgari AR, Hedayati M, Daneshpour MS. Comparative effects of daily and weekly boron supplementation on plasma steroid hormones and proinflammatory cytokines. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2011 Jan;25(1):54-8.
40. Bello M, Guadarrama-García C, Velasco-Silveyra LM, Farfán-García ED,
Soriano-Ursúa MA. Several effects of boron are induced by uncoupling steroid hormones from their transporters in blood. Med Hypotheses. 2018 Sep;118:78-83.
41. Nielsen FH, Hunt CD, Mullen LM, Hunt JR. Effect of dietary boron on mineral, estrogen, and testosterone metabolism in postmenopausal women. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):394-7.
42. Pizzorno L. Nothing Boring About Boron. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2015 Aug;14(4):35-48.
43. Fitoplancton Marino, S.L. [Manufacturer of TetraSOD®] Effects of TetraSOD® as food supplement for peak physical performance.